Example Cross-cluster Configuration
Introduction to Event Driven Addon Distrubution
Sveltos by default will deploy add-ons in the same way an event is detected. Sveltos can be configured for cross-cluster configuration. That means, it will watch for events in a cluster and deploy add-ons in a set of different clusters.
EventTrigger CRD has a field called destinationClusterSelector, a Kubernetes label selector. This field is optional and not set by default. Sveltos default behaviour is to deploy add-ons in the same cluster where the event was detected. If this field is set, Sveltos behaviour will change and when an event is detected in a cluster, add-ons will get deployed in all the clusters matching the label selector destinationClusterSelector.
Example: Cross Cluster Service Discovery
To understand the concept mentioned above, let's have a look at a cross-cluster service discovery example.
Two clusters with the description below are defined.
- GKE cluster (labels env: production) registered with sveltos;
- A cluster-api cluster (label dep: eng) provisioned by docker.
Management Cluster
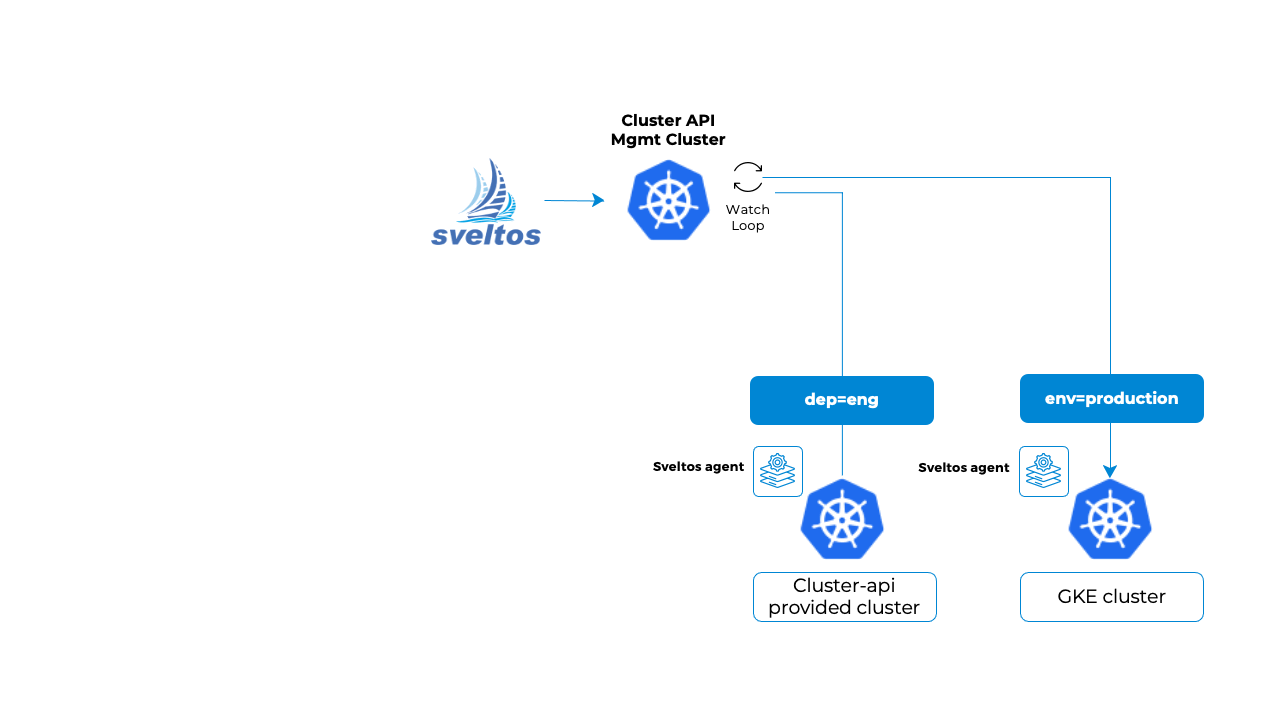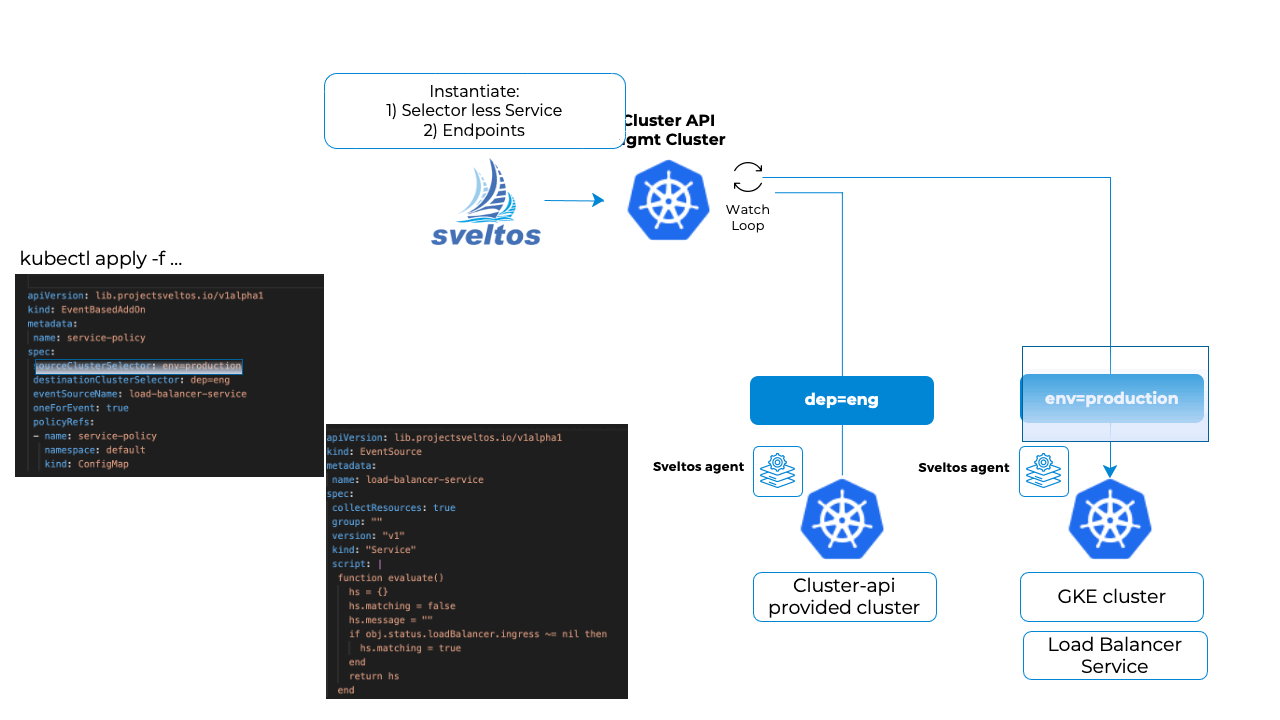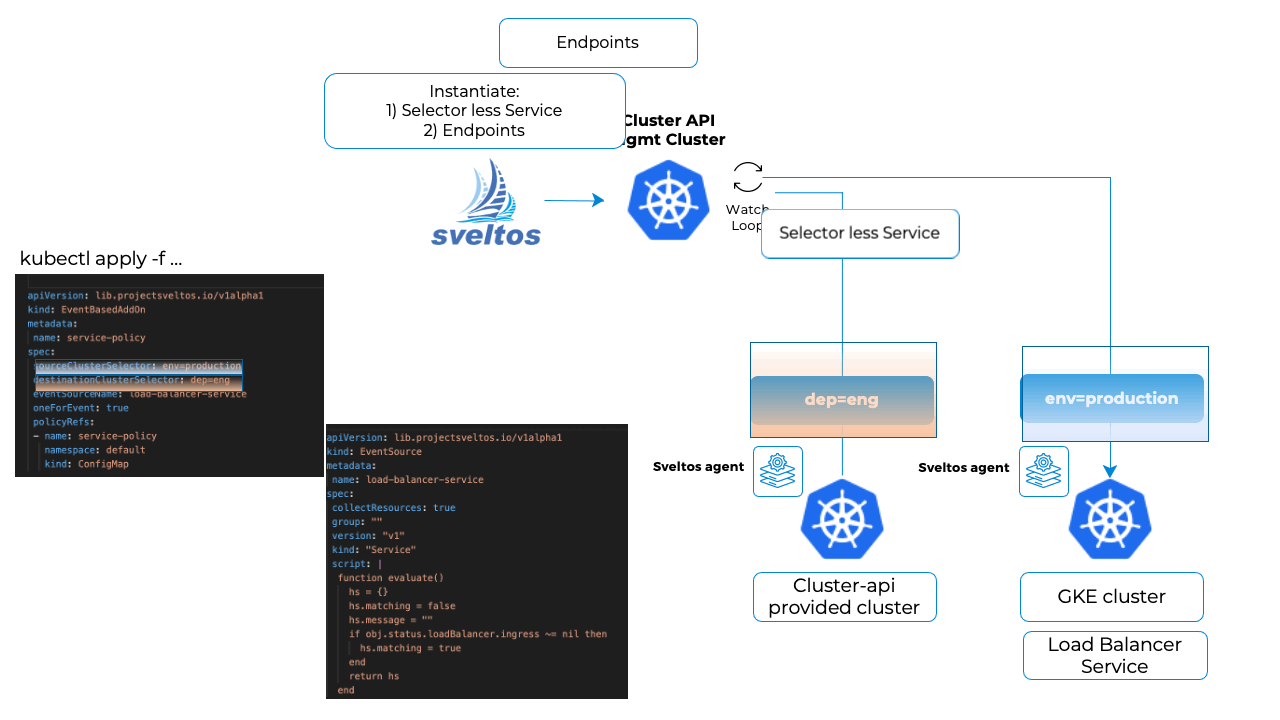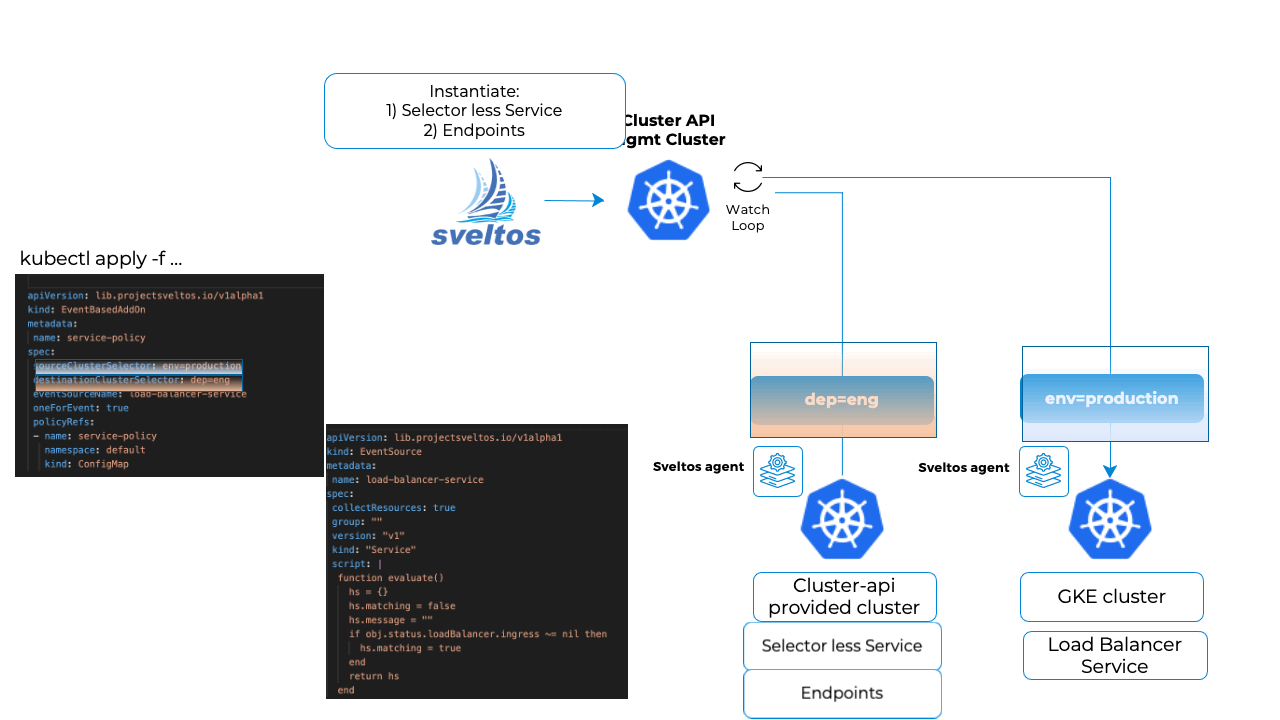
- An EventSource instance that matches any Service with a load balancer IP
Example - EventSource Definition
cat > eventsource.yaml <<EOF
---
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
name: load-balancer-service
spec:
collectResources: true
resourceSelectors:
- group: ""
version: "v1"
kind: "Service"
evaluate: |
function evaluate()
hs = {}
hs.matching = false
hs.message = ""
if obj.status.loadBalancer.ingress ~= nil then
hs.matching = true
end
return hs
end
EOF
- An EventTrigger instance that references the EventSource defined above. It deploys the selector-less Service and corresponding Endpoints in any cluster matching destinationClusterSelector.
Example - EventTrigger Definition
cat > eventtrigger.yaml <<EOF
---
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta11
kind: EventTrigger
metadata:
name: service-policy
spec:
sourceClusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: production
destinationClusterSelector:
matchLabels:
dep: eng
eventSourceName: load-balancer-service
oneForEvent: true
policyRefs:
- name: service-policy
namespace: default
kind: ConfigMap
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: service-policy
namespace: default
annotations:
projectsveltos.io/template: ok
data:
service.yaml: |
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: external-{{ .Resource.metadata.name }}
namespace: external
spec:
selector: {}
ports:
{{ range $port := .Resource.spec.ports }}
- port: {{ $port.port }}
protocol: {{ $port.protocol }}
targetPort: {{ $port.targetPort }}
{{ end }}
endpoint.yaml: |
kind: Endpoints
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: external-{{ .Resource.metadata.name }}
namespace: external
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: {{ (index .Resource.status.loadBalancer.ingress 0).ip }}
ports:
{{ range $port := .Resource.spec.ports }}
- port: {{ $port.port }}
{{ end }}
EOF
As mentioned above, we pass Sveltos a selector-less Service and we then specify our own Endpoints.
The Service and Endpoints are defined as templates and will be instantiated by Sveltos using the information taken from the load-balancer service matching the EventSource (Resource in this context represent a resource matching EventSource).
GKE Cluster
In the GKE cluster we create a deployment and a service of type LoadBalancer.
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-deployment-50001
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: products
department: sales
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: products
department: sales
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: "us-docker.pkg.dev/google-samples/containers/gke/hello-app:2.0"
env:
- name: "PORT"
value: "50001"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-lb-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: products
department: sales
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 60000
targetPort: 50001
The Service will be assigned to an IP address.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-lb-service
namespace: test
...
spec:
...
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: 34.172.32.172
Once this is done, it will match the EventSource. Sveltos will deploy the selector-less Service and the Endpoints in the other cluster, the cluster-api provisioned cluster.
The Endpoints IP address is set to the one assigned to the loadBalancer Service in the GKE cluster.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: external-my-lb-service
namespace: external
...
spec:
ports:
- port: 60000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 50001
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
name: external-my-lb-service
namespace: external
...
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 34.172.32.172
ports:
- port: 60000
protocol: TCP
So at this point now a pod in the cluster-api provisioned cluster can reach the service in the GKE cluster.
Let us create a namespace policy-demo and a busybox pod in the cluster-api provisioned cluster:
Then reach the service in the GKE cluster from the busybox pod in the cluster-api provisioned cluster"
KUBECONFIG=<KIND CLUSTER> kubectl run --namespace=policy-demo access --rm -ti --image busybox /bin/sh
/ #
/ # wget -q external-my-lb-service.external:60000 -O -
Hello, world!
Version: 2.0.0
Hostname: my-deployment-50001-6664b685bc-db728