Configuration Drift detection
Configuration Drift
Configuration drift is a commonly used term to describe a change that takes place in an environment. Drift is an issue as it causes systems and parts of a system which supposed to be consistent, to become inconsistent and unpredictable. In our case, configuration drift is a change of a resource deployed by Sveltos down the managed clusters.
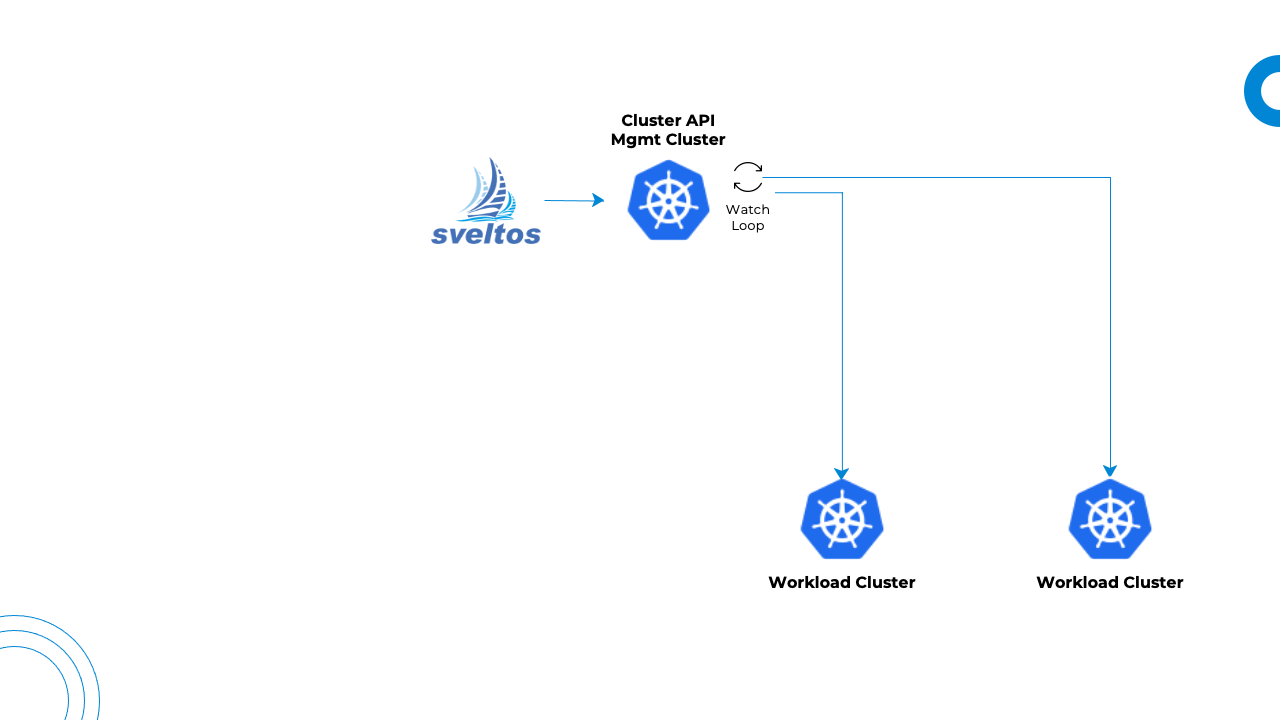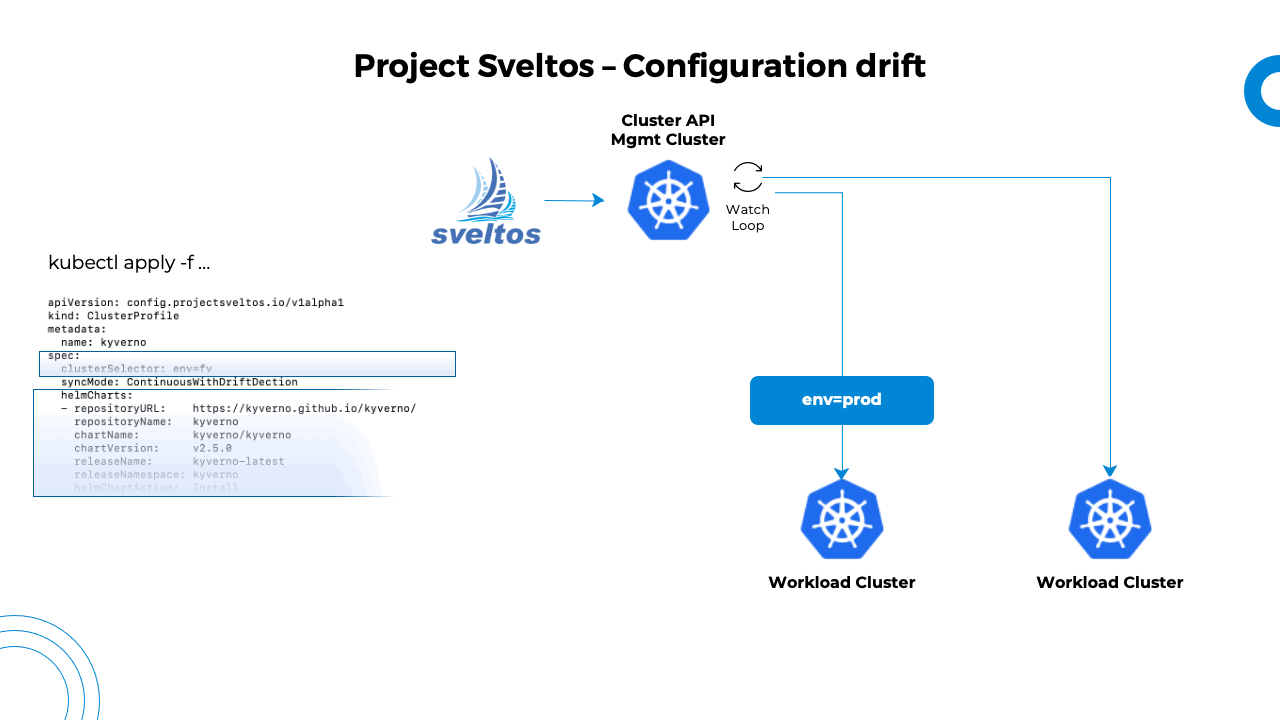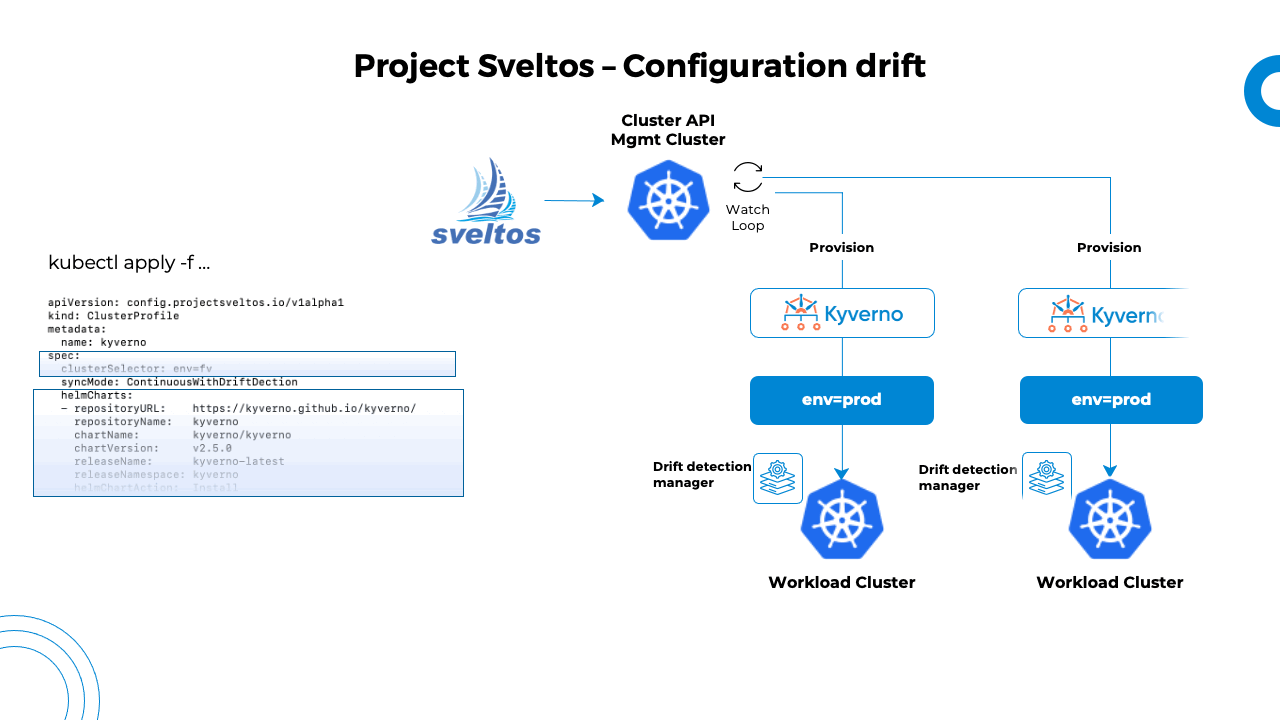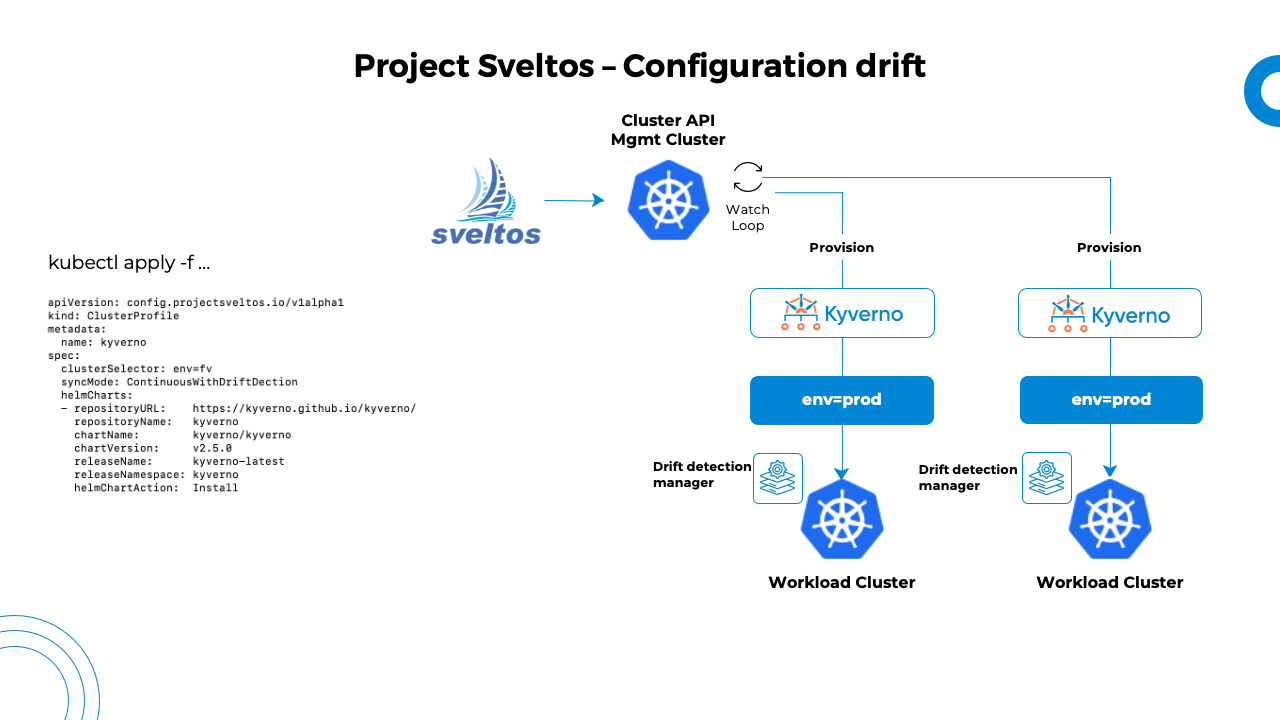
Sveltos allows users to set the sync mode within a ClusterProfile to ContinuousWithDriftDetection. It enables Sveltos to monitor the state of managed clusters and detect configuration drift for any of the resources deployed by a ClusterProfile.
---
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: deploy-kyverno
spec:
syncMode: ContinuousWithDriftDetection
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
repositoryName: kyverno
chartName: kyverno/kyverno
chartVersion: v3.3.3
releaseName: kyverno-latest
releaseNamespace: kyverno
helmChartAction: Install
When Sveltos detects a configuration drift, it will automatically re-sync the cluster state back to its original state which is described in the management cluster. Sveltos deploys a service in each managed cluster and configures it with a list of Kubernetes resources deployed for each ClusterProfile in SyncModeContinuousWithDriftDetection mode.
The service starts a watcher for each GroupVersionKind with at least one resource to watch. When any watched resources are modified (labels, annotations, spec or rules sections), the service notifies the management cluster about potential configuration drifts. The management cluster then reacts by redeploying affected ClusterProfiles.
This way, Sveltos ensures that the systems are always consistent and predictable, preventing unexpected issues caused by the configuration drifts.
Ignore Annotation
You can stop certain resources from being tracked for configuration drift. This is done by adding a special annotation projectsveltos.io/driftDetectionIgnore to those resources.
For instance, following ClusterProfile will deploy Kyverno helm chart. Patches are used to apply annotation to the Kyverno kyverno-admission-controller deployment.
This means any changes made to resources deployed by the Helm chart itself will be flagged as a configuration drift. However, any modifications directly to the kyverno-admission-controller deployment won't be detected as drift.
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: deploy-kyverno
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: fv
syncMode: ContinuousWithDriftDetection
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
repositoryName: kyverno
chartName: kyverno/kyverno
chartVersion: v3.3.3
releaseName: kyverno-latest
releaseNamespace: kyverno
helmChartAction: Install
patches:
- target:
group: apps
version: v1
kind: Deployment
name: "kyverno-admission-controller"
patch: |
- op: add
path: /metadata/annotations/projectsveltos.io~1driftDetectionIgnore
value: "ok"
Ignore Fields
You can optionally specify fields to be excluded from drift detection using JSON Pointers.
Here's an example configuration in YAML format:
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: prod
syncMode: ContinuousWithDriftDetection
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://helm.nginx.com/stable/
repositoryName: nginx-stable
chartName: nginx-stable/nginx-ingress
chartVersion: 1.3.1
releaseName: nginx-latest
releaseNamespace: nginx
helmChartAction: Install
driftExclusions:
- paths:
- "/spec/replicas"
target:
kind: Deployment
Customize drift-detection-manager configuration
In some cases, we might want to tailor the deployment of the drift-detection-manager. To achieve this, the addon-controller pod accepts a new argument named drift-detection-config.
The drift-detection-config argument points to a ConfigMap within the projectsveltos namespace. The ConfigMap holds patches that will be applied to the drift-detection-manager before its deployment in the managed cluster.
ConfigMap Example
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: drift-detection
namespace: projectsveltos
data:
patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: drift-detection-manager
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: manager
image: registry.company.io/projectsveltos/drift-detection-manager:dev
resources:
requests:
memory: 256Mi
Along with creating the ConfigMap, we also need to configure the addon-controller deployment to use it. To do this, add the below argument to the deployment.
With the defined configuration, the drift-detection-manager will get deployed in each managed cluster with the below settings.
- Request memory: 256Mi
- Image: projectsveltos/drift-detection-manager:dev
Tip
If you are deploying Sveltos using the official Helm chart and need to patch the drift-detection-manager before deployment, include the necessary values in your values.yaml file.
$ helm install projectsveltos projectsveltos/projectsveltos -n projectsveltos -f values.yaml
addonController:
controller:
args:
- --diagnostics-address=:8443
- --report-mode=0
- --shard-key=
- --v=5
- --version=v0.44.0
argsAgentMgmtCluster:
- --diagnostics-address=:8443
- --report-mode=0
- --agent-in-mgmt-cluster
- --shard-key=
- --v=5
- --version=v0.44.0
- --drift-detection-config=drift-detection-config
agent:
managementCluster: true