Distribute Add-ons
What is Sveltos?
Sveltos is a set of Kubernetes controllers that run in the management cluster. From the management cluster, Sveltos can manage add-ons and applications on a fleet of managed Kubernetes clusters.
Sveltos comes with support to automatically discover ClusterAPI powered clusters, but it doesn't stop there. You can easily register any other cluster (on-prem, Cloud) and manage Kubernetes add-ons seamlessly.
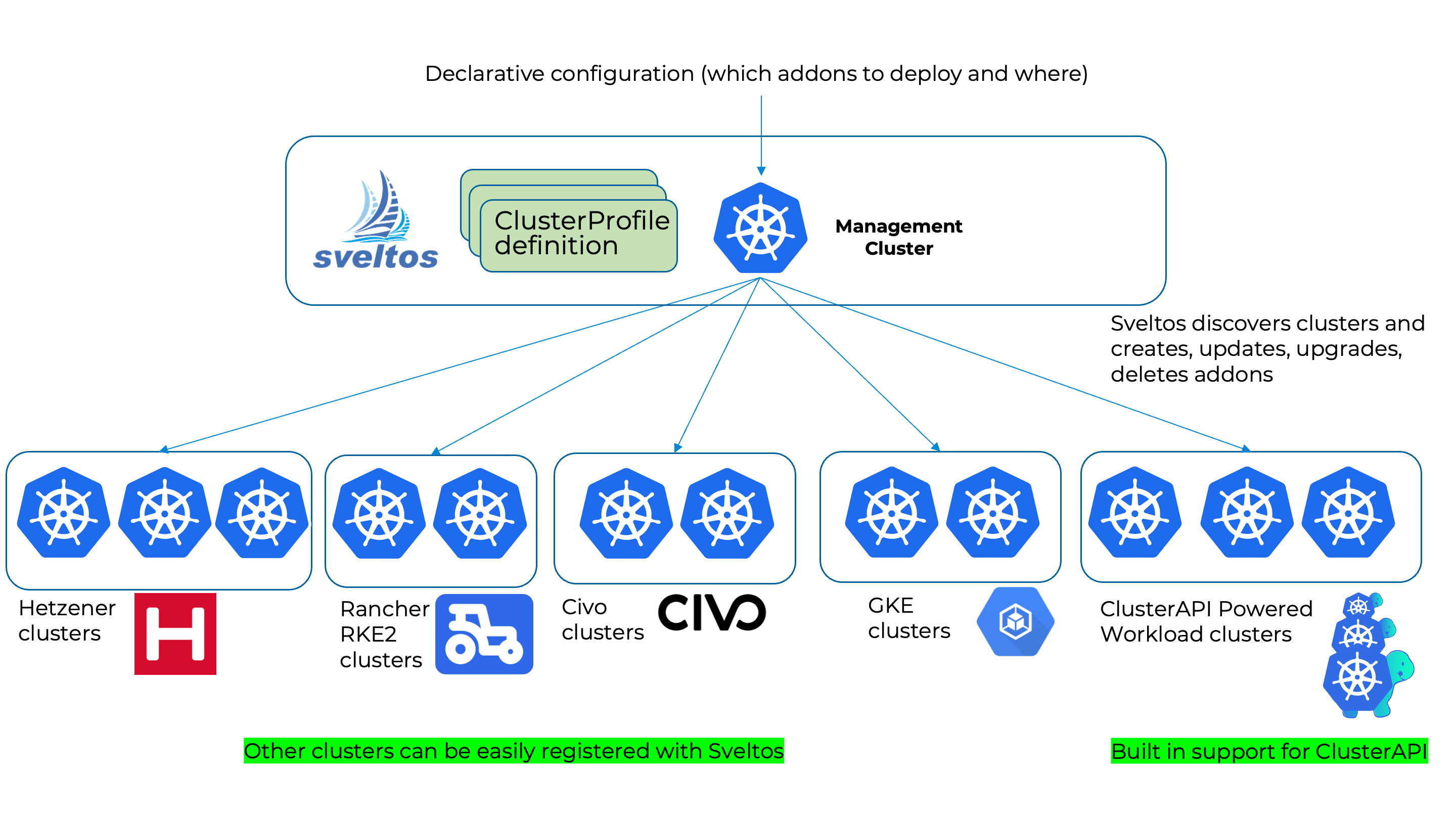
How it works?
ClusterProfile and Profile are the CustomerResourceDefinitions used to instruct Sveltos which add-ons to deploy on a set of clusters.
-
ClusterProfile: It is a cluster-wide resource. It can match any cluster and reference any resource regardless of their namespace.
-
Profile: It is a namespace-scoped resource that is specific to a single namespace. It can only match clusters and reference resources within its own namespace.
By creating a ClusterProfile instance, you can easily deploy the below across a set of Kubernetes clusters.
- Helm charts
- Resources assembled with Kustomize
- Raw Kubernetes YAML/JSON manifests
Define which Kubernetes add-ons to deploy and where:
- Select one or more clusters using a Kubernetes label selector;
- List the Kubernetes add-ons that need to be deployed on selected clusters
It is as simple as that!
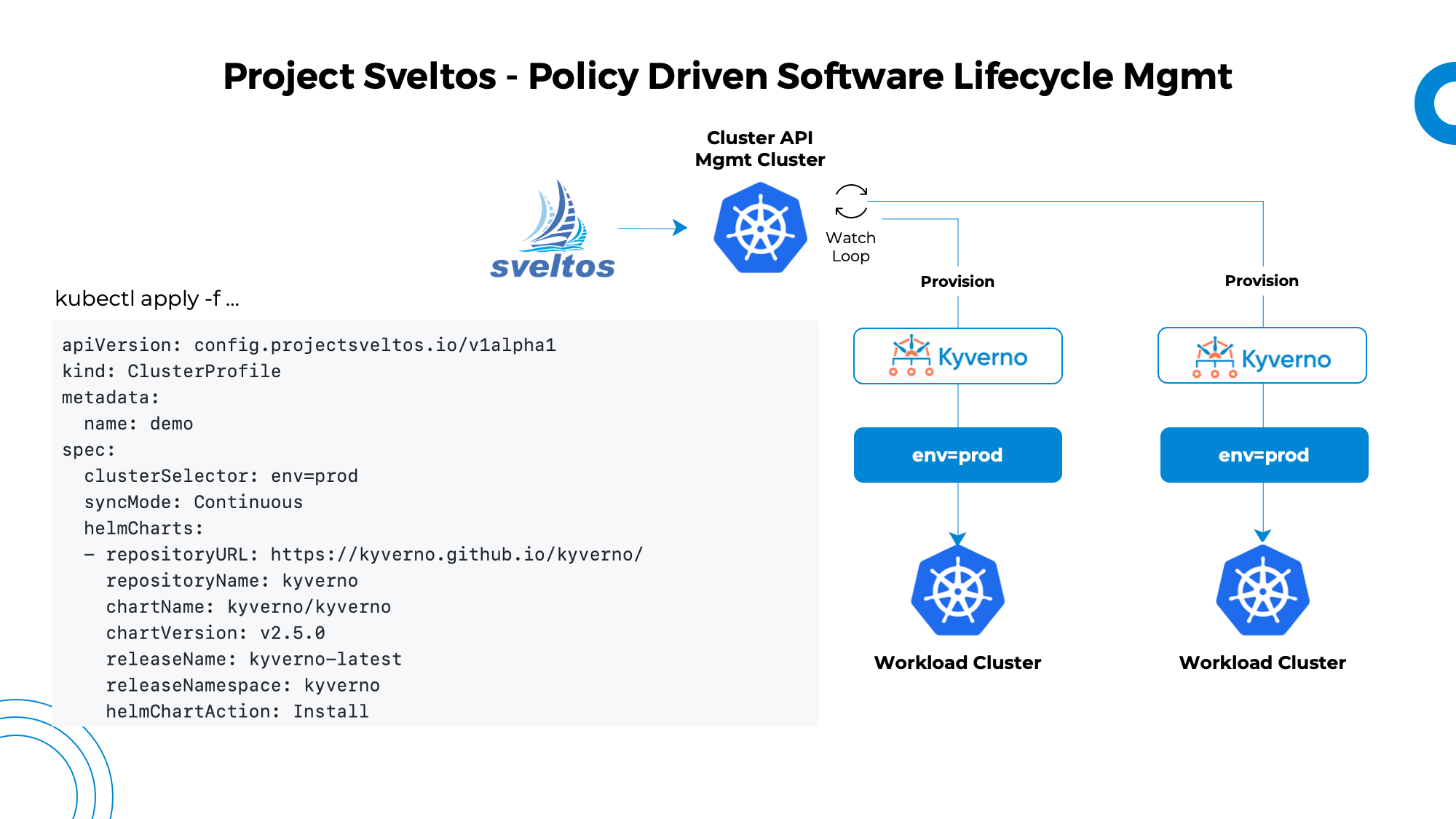
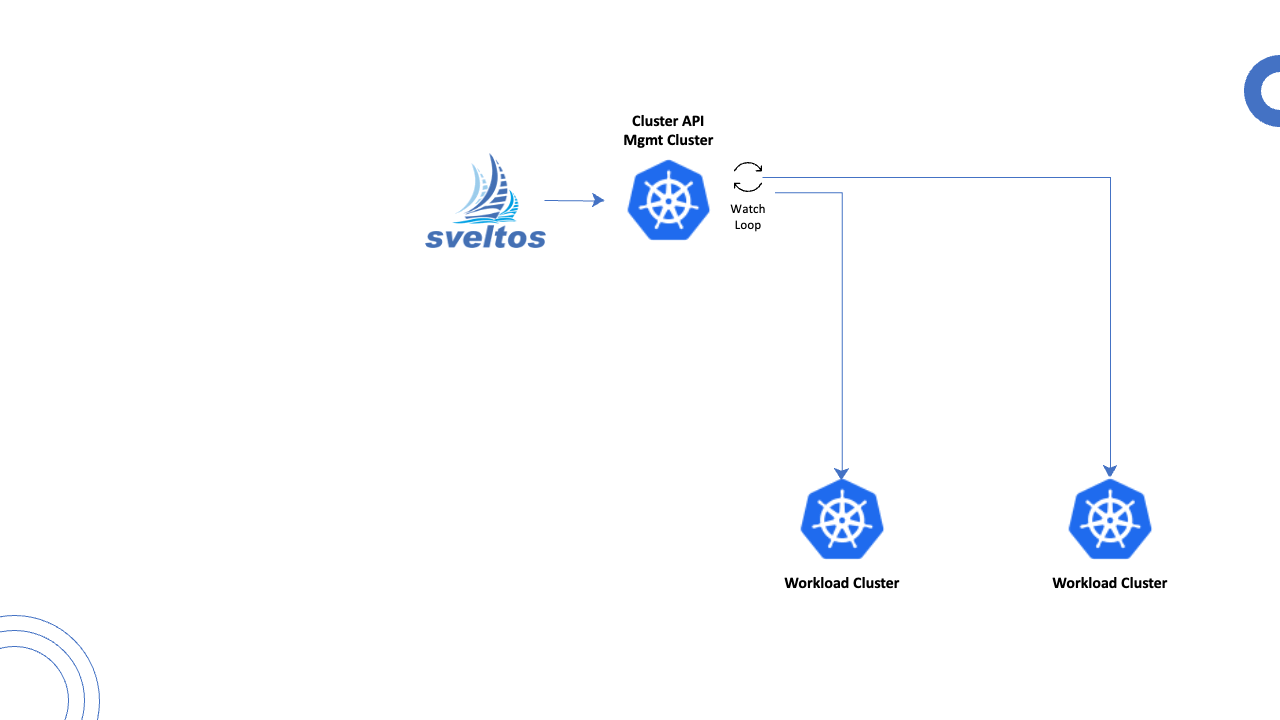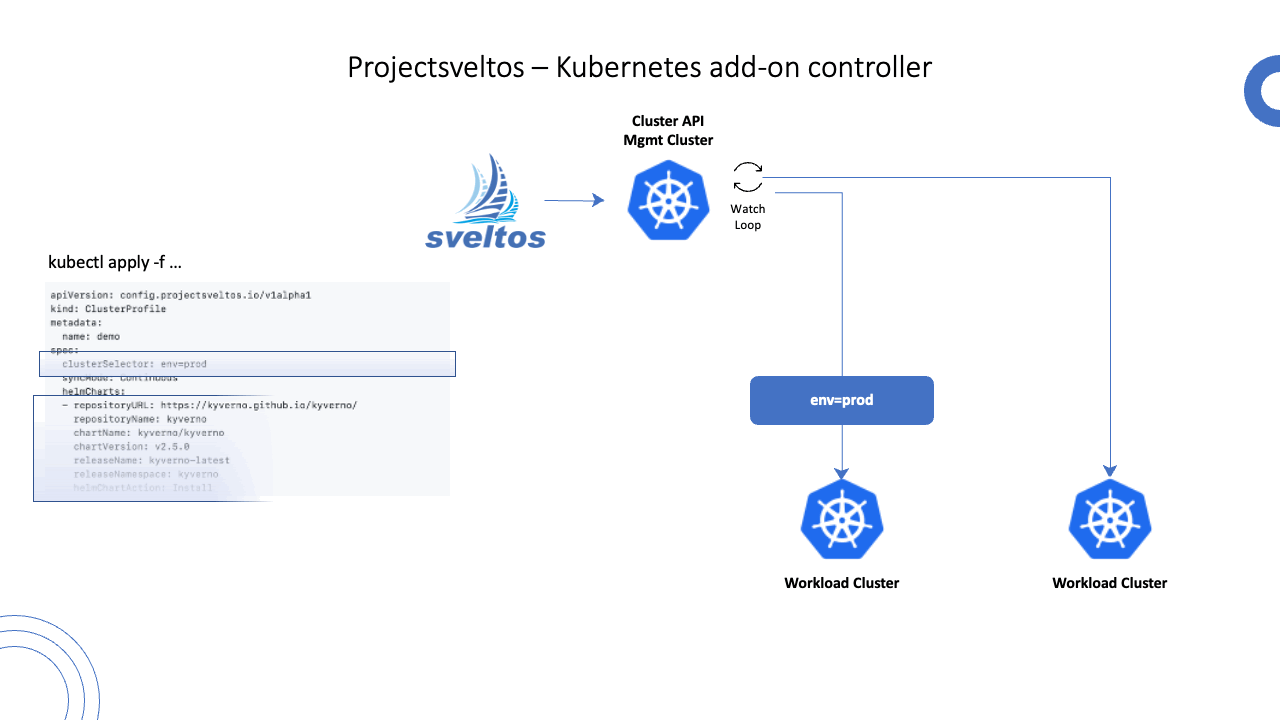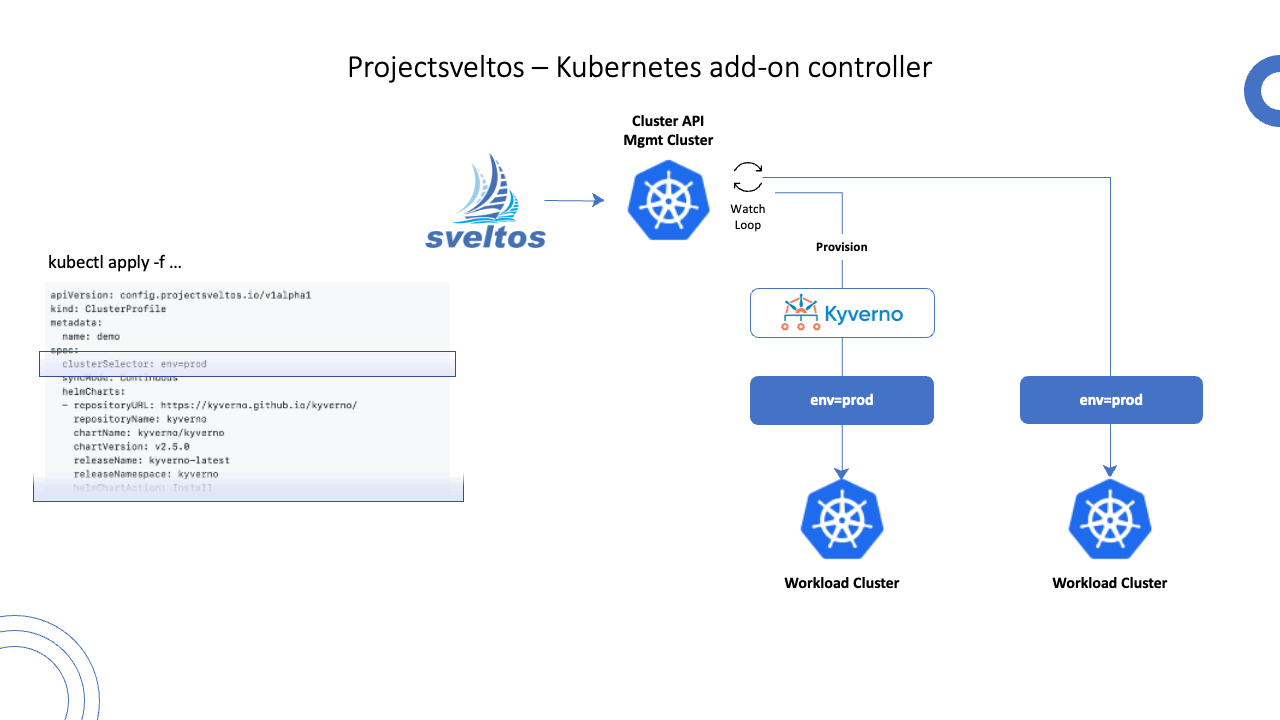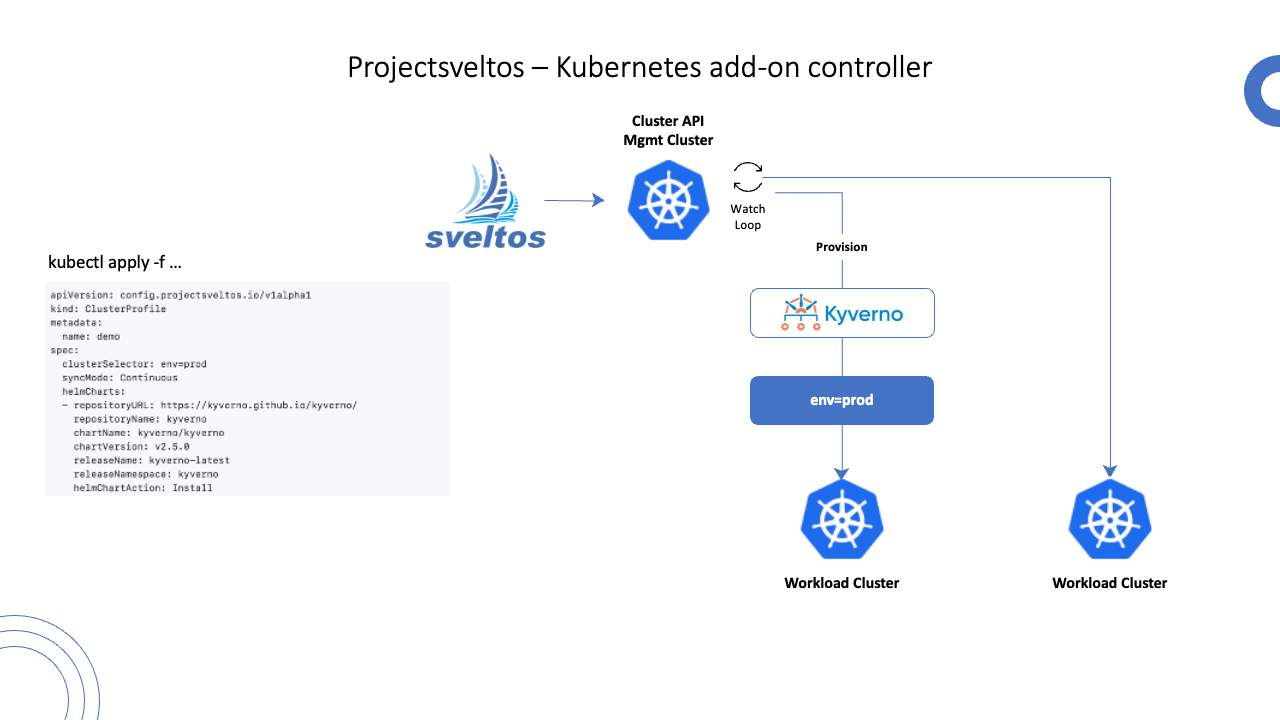
Example: Kyverno ClusterProfile
The below example deploys a Kyverno helm chart in every cluster with the label selector set to env=prod.
Step 1: Register Clusters
The first step is to ensure the CAPI clusters are successfully registered with Sveltos. If you have not registered the clusters yet, follow the instructions mentioned here.
If you have already registered the CAPI clusters, ensure they are listed and ready to receive add-ons.
$ kubectl get sveltosclusters -n projectsveltos --show-labels
NAME READY VERSION LABELS
cluster12 true v1.26.9+rke2r1 sveltos-agent=present
cluster13 true v1.26.9+rke2r1 sveltos-agent=present
Note
The CAPI clusters are registered in the projectsveltos namespace. If you register the clusters in a different namespace, update the command above.
Step 2: Add Kubernetes Label
The second step is to assign a specific label to the Sveltos Clusters to receive specific add-ons. In this example, we will assign the label env=prod.
$ kubectl label sveltosclusters cluster12 env=prod -n projectsveltos
$ kubectl label sveltosclusters cluster13 env=prod -n projectsveltos
$ kubectl get sveltosclusters -n projectsveltos --show-labels
NAME READY VERSION LABELS
cluster12 true v1.26.9+rke2r1 env=prod,sveltos-agent=present
cluster13 true v1.26.9+rke2r1 env=prod,sveltos-agent=present
Tip
Starting v0.29.0, sveltosctl supports label assignment directly with the Sveltos cluster registration process. More details here.
Step 3: Create the ClusterProfile
The third step is to create a ClusterProfile Kubernetes resource and apply it to the management cluster.
cat > clusterprofile_kyverno.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: kyverno
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: prod
syncMode: Continuous
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
repositoryName: kyverno
chartName: kyverno/kyverno
chartVersion: v3.3.3
releaseName: kyverno-latest
releaseNamespace: kyverno
helmChartAction: Install
EOF
$ kubectl apply -f "clusterprofile_kyverno.yaml"
$ sveltosctl show addons
+--------------------------+---------------+-----------+----------------+---------+-------------------------------+------------------+
| CLUSTER | RESOURCE TYPE | NAMESPACE | NAME | VERSION | TIME | CLUSTER PROFILES |
+--------------------------+---------------+-----------+----------------+---------+-------------------------------+------------------+
| projectsveltos/cluster12 | helm chart | kyverno | kyverno-latest | 3.2.5 | 2023-12-16 00:14:17 -0800 PST | kyverno |
| projectsveltos/cluster13 | helm chart | kyverno | kyverno-latest | 3.2.5 | 2023-12-16 00:14:17 -0800 PST | kyverno |
+--------------------------+---------------+-----------+----------------+---------+-------------------------------+------------------+
Note
If you are not aware of the sveltosctl utility, have a look at the installation documentation found here.
More Resources
For a quick add-ons example, watch the Sveltos introduction video on YouTube.