Tenants Sharing Clusters
Introduction to Multitenancy
With Sveltos, a management cluster is used to manage add-ons in tens of clusters. When managing tens of clusters, multitenancy plays an important role.
Common forms of multitenancy
- Share a cluster between multiple teams within an organization, each of whom may operate one or more workloads. These workloads frequently need to communicate with each other, and with other workloads located on the same or different clusters;
- One (or more) cluster(s) fully reserved for an organization.
Defined Roles
- Platform admin: Is the admin with the cluster-admin access to all the managed clusters;
- Tenant admin: Is the admin with access to the clusters/namespaces assigned to them by the platform admin. Tenant admin manages applications for a tenant.
Sveltos Solution
- Platform admin onboards tenant admins and easily define what each tenant can do in which clusters;
- Tenant admin manage tenant applications from a single place, the management cluster.
Sveltos RoleRequest CRD
RoleRequest is the CRD introduced by Sveltos to allow platform admins to grant permissions to various tenant admins.
Based on the above YAML definition, we specify the below fields:
serviceAccountName: The service account the permission will be applied to;serviceAccountNamespace: The namespace the service account has been deployed in the management clusterclusterSelector: This is a Kubernetes label selector. Sveltos uses the label to detect all the clusters where permissions need to be granted;roleRefs: References ConfigMaps/Secrets each containing one or more Kubernetes ClusterRoles/Roles defining the permissions to be granted.
An example of a ConfigMap containing a ClusterRole granting definition with full edit permissions can be found below.
More Examples
More examples can be found here.
Example - ClusterProfile Definition
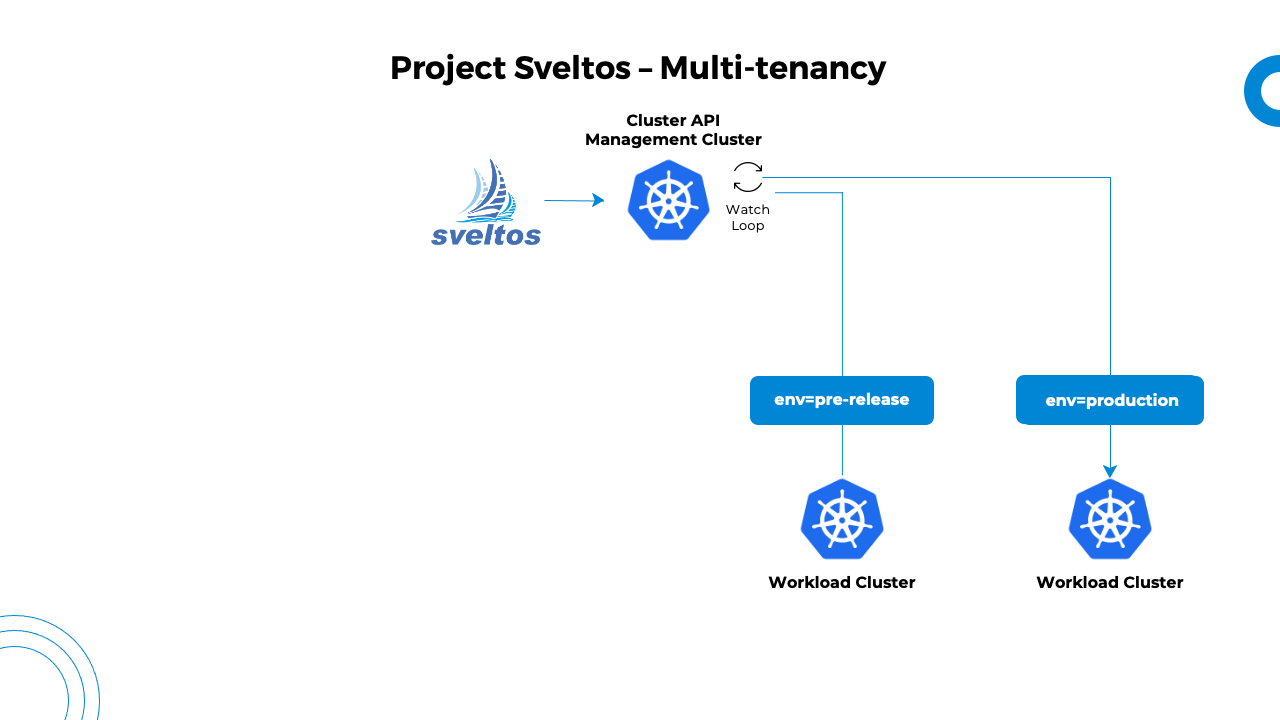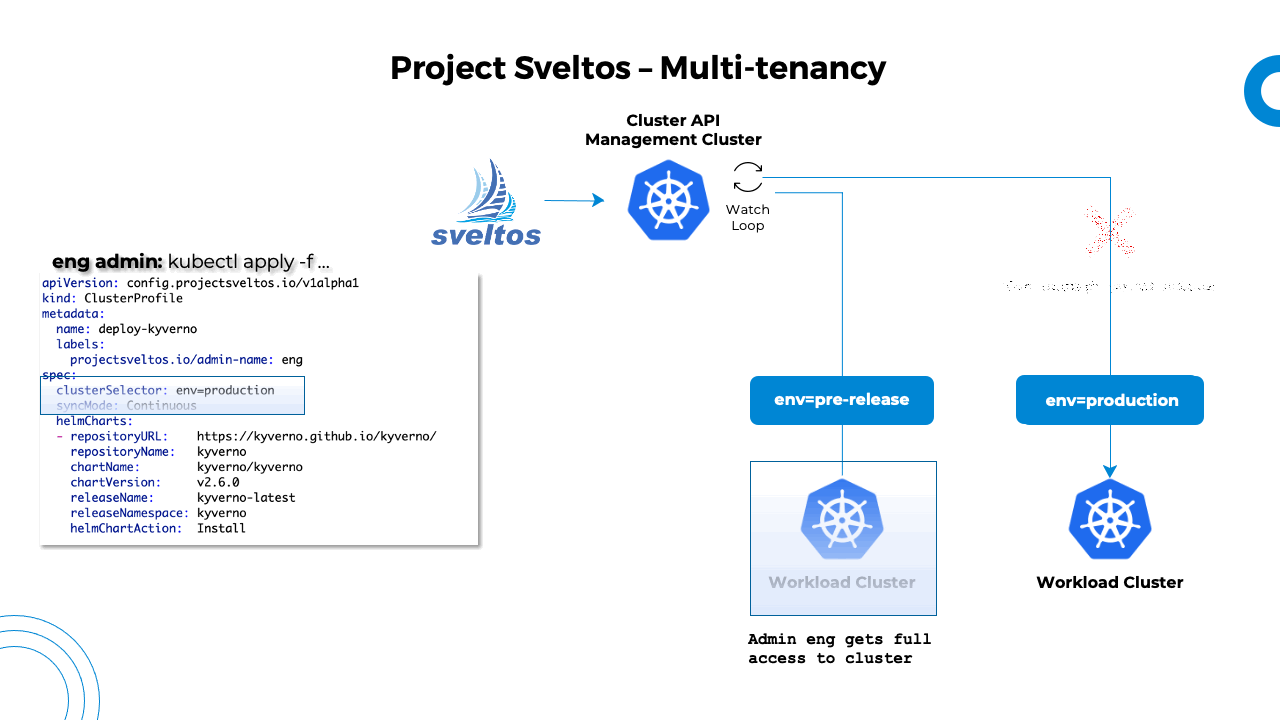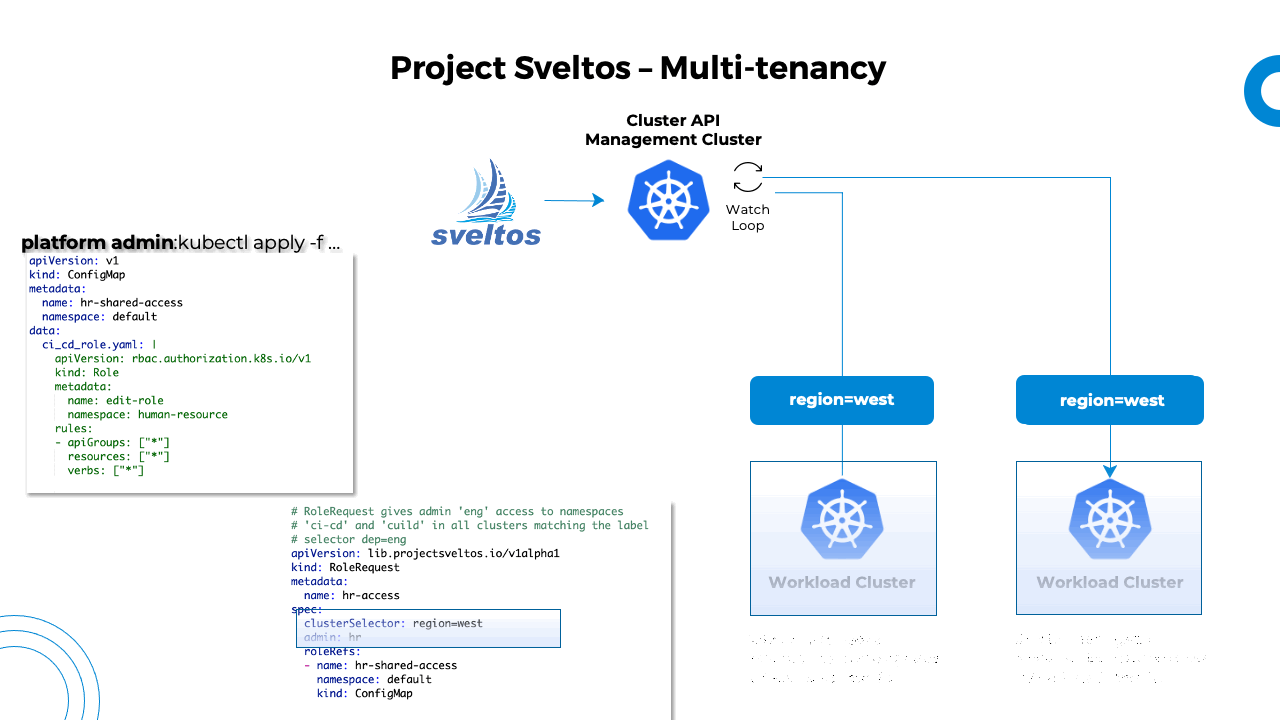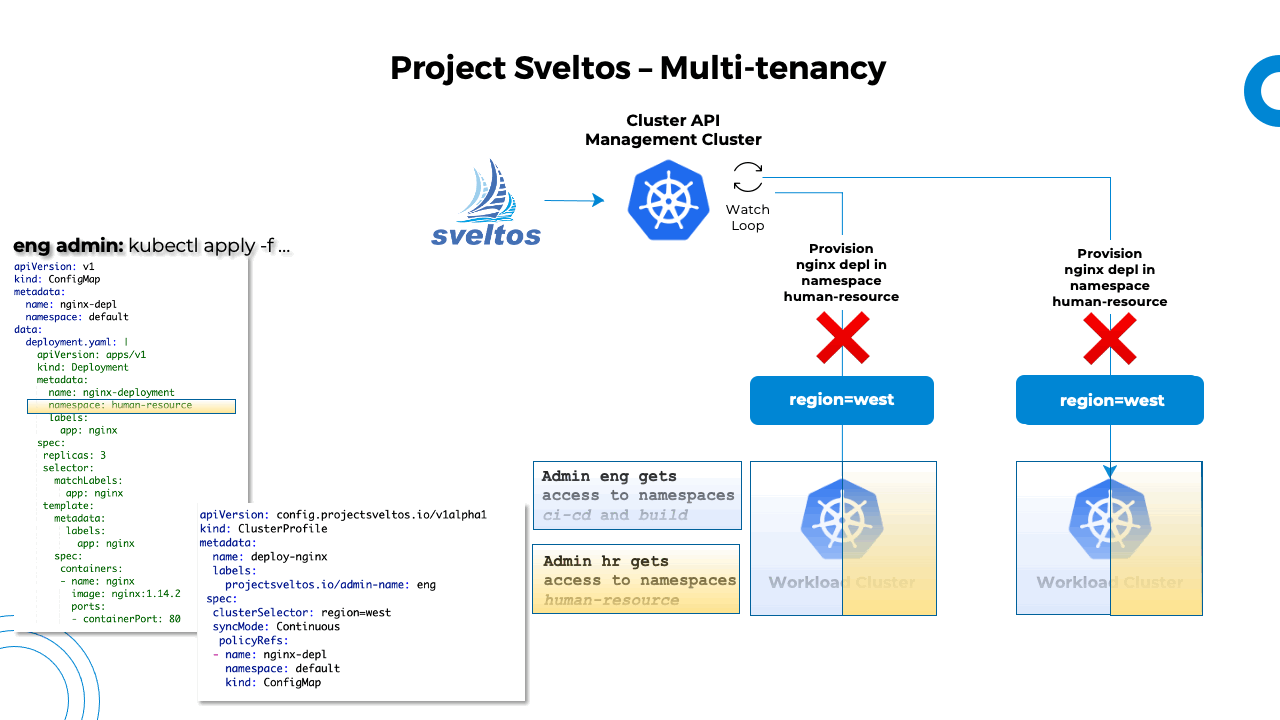
After a tenant is onboarded by the platform admin, the service account created in the step above can use a ClusterProfiles and Sveltos will take care of deploying the defined resources to all matching clusters.
Sveltos expects the following labels to be set on each ClusterProfile.
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-name: <service account name>
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-namespace: <service account defined namespace>
If:
- Each tenant admin is a ServiceAccount in the management cluster;
- Kyverno is deployed in the management cluster;
Sveltos suggests using the below Kyverno ClusterPolicy, which will take care of adding proper labels to each ClusterProfile at creation time.
---
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: add-labels
annotations:
policies.kyverno.io/title: Add Labels
policies.kyverno.io/description: >-
Adds projectsveltos.io/admin-name label on each ClusterProfile
created by tenant admin. It assumes each tenant admin is
represented in the management cluster by a ServiceAccount.
spec:
background: false
rules:
- exclude:
any:
- clusterRoles:
- cluster-admin
match:
all:
- resources:
kinds:
- ClusterProfile
mutate:
patchStrategicMerge:
metadata:
labels:
+(projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-name): '{{serviceAccountName}}'
+(projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-namespace): '{{serviceAccountNamespace}}'
name: add-labels
validationFailureAction: enforce
Example - Tenant Cluster Reservation
In the example below, all clusters matching the Kubernetes label selector org=foo.io will be assigned to the service account with the name foo.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: full-access
namespace: default
data:
role.yaml: |
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: foo-full-access
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleRequest
metadata:
name: full-access
spec:
serviceAccountName: "foo"
serviceAccountNamespace: "default"
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
org: foo.io
roleRefs:
- name: full-access
namespace: default
kind: ConfigMap
We can use of the sveltosctl to check the permissions given to the service account foo. We expect the service account to have full access to the managed cluster with the label set to env:production
$ sveltosctl show admin-rbac
+-------------------------------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+
| CLUSTER | ADMIN | NAMESPACE | API GROUPS | RESOURCES | RESOURCE NAMES | VERBS |
+-------------------------------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+
| SveltosCluster:gke/production | foo | * | * | * | * | * |
+-------------------------------+--------------+-----------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+
As soon as the service account foo posts the below ClusterProfile, Sveltos will deploy Kyverno in any cluster matching the label selector set to org=foo.io.
---
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: deploy-kyverno
labels:
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-name: foo
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-namespace: default
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
org: foo.io
syncMode: Continuous
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
repositoryName: kyverno
chartName: kyverno/kyverno
chartVersion: v3.3.3
releaseName: kyverno-latest
releaseNamespace: kyverno
helmChartAction: Install
If the same service account tries to deploy Kyverno in a cluster not assigned to it, Sveltos will fail the deployment.
For instance, if the ClusterProfile.Spec.ClusterSelector is set to org=bar.io, the deployment will fail.
---
apiVersion: config.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterProfile
metadata:
name: deploy-kyverno
labels:
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-name: foo
projectsveltos.io/serviceaccount-namespace: default
spec:
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
org: bar.io
syncMode: Continuous
helmCharts:
- repositoryURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
repositoryName: kyverno
chartName: kyverno/kyverno
chartVersion: v3.3.3
releaseName: kyverno-latest
releaseNamespace: kyverno
helmChartAction: Install
Example - Share Cluster Between Tenants
In the below examples, all clusters matching the label selector env=internal are shared between two tenants:
- Service Account eng is granted full access to namespaces foo-eng and foo-hr
- Service Account hr is granted full access to namespace bar-resource
# ConfigMap contains a Role which gives
# full access to namespaces ci-cd and build
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: foo-shared-access
namespace: default
data:
ci_cd_role.yaml: |
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: edit-role
namespace: foo-eng
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
build_role.yaml: |
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: edit-role
namespace: foo-hr
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
# RoleRequest gives the service account 'eng' access to namespaces
# 'ci-cd' and 'build' in all clusters matching the label
# selector env=internal
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleRequest
metadata:
name: foo-access
spec:
serviceAccountName: "eng"
serviceAccountNamespace: "default"
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: internal
roleRefs:
- name: foo-shared-access
namespace: default
kind: ConfigMap
---
# ConfigMap contains a Role which gives
# full access to the namespace human-resource
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: bar-shared-access
namespace: default
data:
ci_cd_role.yaml: |
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: edit-role
namespace: bar-resource
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
# RoleRequest gives service account 'hr' access to the namespace
# 'human-resource' in all clusters matching the label
# selector env=internal
apiVersion: lib.projectsveltos.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleRequest
metadata:
name: bar-access
spec:
serviceAccountName: "hr"
serviceAccountNamespace: "default"
clusterSelector:
matchLabels:
env: internal
roleRefs:
- name: bar-shared-access
namespace: default
kind: ConfigMap
Display Tenant Admin Permissions
Sveltos heavily focuses on the visibility of the clusters. The Sveltosctl can be used to display permissions granted to each tenant admin in each managed cluster.
If we have two clusters, a ClusterAPI powered and a SveltosCluster, both matching the label selector
env=internal and we post the RoleRequests, we get the below output.
$ sveltosctl show admin-rbac
+---------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+
| CLUSTER | ADMIN | NAMESPACE | API GROUPS | RESOURCES | RESOURCE NAMES | VERBS |
+---------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+
| Cluster:default/sveltos-management-workload | eng | build | * | * | * | * |
| Cluster:default/sveltos-management-workload | eng | ci-cd | * | * | * | * |
| Cluster:default/sveltos-management-workload | hr | human-resource | * | * | * | * |
| SveltosCluster:gke/prod-cluster | eng | build | * | * | * | * |
| SveltosCluster:gke/prod-cluster | eng | ci-cd | * | * | * | * |
| SveltosCluster:gke/prod-cluster | hr | human-resource | * | * | * | * |
+---------------------------------------------+-------+----------------+------------+-----------+----------------+-------+